Excerpted from Champlain’s Voyages to New France 1632
October 10, 1615 near present day Syracuse, New York
Champlain’s lack of understanding of Aborginal language contributed to his frustration in battle alongside the Wendat (Huron) people. Champlain gave orders during the battle in French, and when the orders were ignored, assumed that the Wendat were undisciplined warriors. Champlain also did not understand Aboriginal rules of battle which contributed to his frustration.
At three o’clock in the afternoon, we arrived before the fort of [the Huron and Algonkians’] enemies, where the savages made some skirmishes with each other, although our design was not to disclose ourselves until the next day, which however the impatience of our savages would not permit, both on account of their desire to see fire opened upon their enemies, and
also that they might rescue some of their own men who had become too closely engaged, and were hotly pressed. Then I approached the enemy, and although I had only a few men, yet we showed them what they had never seen nor heard before; for, as soon as they saw us and heard the arquebus [muskel shots and the balls whizzing in their ears, they withdrew speedily
to their fort, carrying the dead and wounded in this charge. We also withdrew to our main body, with five or six wounded, one of whom died.
This done, we withdrew to the distance of cannon range, out of sight of the enemy, but contrary to my advice and to what they had promised me. This moved me to address them very rough and angry words in order to incite them to do their duty, foreseeing that if everything should go according to their whim and the guidance of their council, their utter ruin would be the result. Nevertheless I did not fail to send to them and propose means which they should use in order to get possession of their enemies.
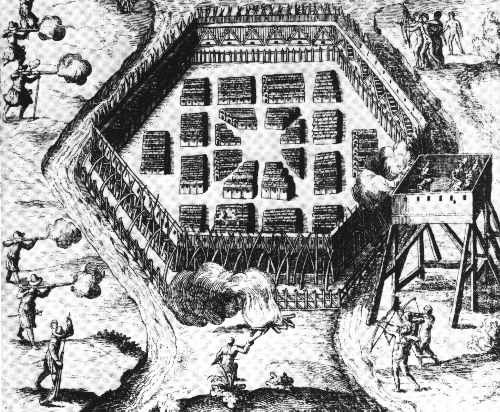
These were, to make with certain kinds of wood a cavalier [an elevated, enclosed wooden platform] which would be higher than the palisades. Upon his were to be placed four or five of our arquebusiers, who should keep up a onstant fire over their palisades and galleries, which were well provided vith stones, and by this means dislodge the enemy who might attack us
frm their galleries. . . . This proposition they thought good and very easonable, and immediately proceeded to carry them out as I directed. “[The next day] we approached to attack the village, our cavalier being armed by two hundred of the strongest men, who put it down before the village at a pike’s length off. I ordered three arquebusiers to mount upon it, who were well protected from the arrows and stones that could be shot or hurled at them. Meanwhile the enemy ‘did not fail to send a large number of arrows which did not miss, and a great many stones, which they hurled from their palisades. Nevertheless a hot fire of arquebusiers forced them to dislodge and abandon their galleries, in consequence of the cavalier which uncovered them, they not venturing to show themselves, but fighting under shelter. Now when the cavalier was carried forward, instead of bringing upthe mantelets [large wooden shields] according to order, including . . . one under cover of which we were to set [a] fire, they abandoned them and began to scream at their enemies, shooting arrows into the fort, which in my opinion did little harm to the enemy.
But we must excuse them, for they are not warriors, and besides will have no discipline nor correction, and will do only what they please. Accordingly one of them set fire inconsiderately to the wood placed against the fort of the enemy, quite the wrong way and in the face of the wind, so that it produced no effect. “This fire being out, the greater part of the savages began to carry wood against the palisades, but in so small quantity that the fire could have no great effect. There also arose such disorder among them that one could not understand another, which greatly troubled me. In vain did I shout in their ears and remonstrate to my utmost with them as to the danger to which they exposed themselves by their bad behavior, but on account of the great noise they made they heard nothing. Seeing that shouting would only burst my head, and that my remonstrances were useless for putting a stop to the disorder, I did nothing more, but determined together with my men to do what we could, and fire upon such as we could see. .
e were engaged in this combat about three hours, in which two of our chiefs and leading warriors were wounded, namely, one called Ochateguam and another Orani, together with some fifteen common warriors. The others, seeing their men and some of the chiefs wounded, now began to talk of a retreat without farther fighting, in expectation of the five hundred men, whose arrival could not be much delayed. Thus they retreated, a disorderly rabble.
“Moreover the chiefs have in fact no absolute control over their men, who are governed by their own will and follow their own fancy, which is the cause of their disorder and the ruin of all their undertakings; for, having determined upon anything with their leaders, it needs only the whim of a villain, or nothing at all, to lead them to break it off and form a new plan. Thus there is no concert of action among them, as can be seen by this expedition.